25-Nov-2025
Presto Instruments
It is very useful to know the acidity and alkalinity of liquids in many scientific, industrial, and everyday contexts. The appropriate pH is very important to know if it is safe drinking water, a soil's health and quality of food, or the chemical industry.
That is where the pH meter will enter the picture: a device that should provide accurate measurements to make the necessary decisions, improve safety, and maintain consistency. The ease of use of its design, coupled with its extensive application base, has made the pH meter a significant tool in the laboratory, industry, and environmental monitoring.
A pH meter is a precise electronic device to measure how acidic or alkaline a solution is by detecting the hydrogen ion concentration. A reading less than 7 means that it is an acid; a reading of 7 is neutral; and a reading greater than 7 means that it is an alkaline solution.
pH meters have now been invaluable in numerous areas and practices, including quality control, research, productivity, and safety in areas of agriculture, food safety and production, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment applications.
The pH meter's full form is "Potential of Hydrogen," or "Power of Hydrogen." A pH meter is a device that measures the pH of a solution to assess whether it is acidic or basic.
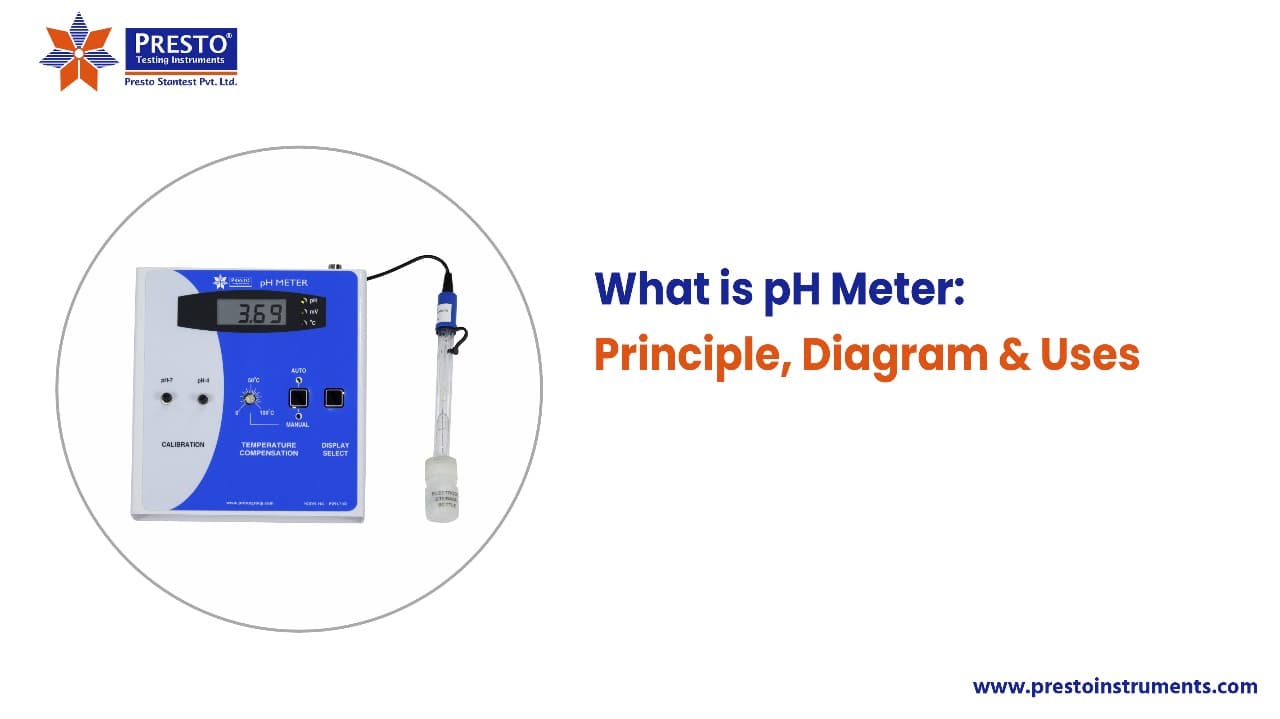
A pH meter diagram includes a glass electrode that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions. It also has a reference electrode that provides a stable reference voltage for the glass electrode to determine the pH. The setup features a digital display or meter that shows the pH reading.
The core components in a pH meter diagram are as follows:
In the PH meter working principle, the relative degree of hydrogen ions (H) in a solution is measured. The pH meter measures the difference in voltages between a pH sensitive electrode; a glass electrode and a reference electrode. The produced voltage relates directly to the pH of the solution as described by the Nernst equation. This electrical signal gets converted into a numerical pH value.
Place the probe of a pH meter, consisting of both the glass and reference electrodes, into the solution for testing. Make sure that both the glass bulb and the reference junction are completely involved.
At the tip of the glass electrode, there is a thin porous glass membrane that interacts with H+ ions in the sample. This interaction produces an exchange of ions across the solution and the glass and produces a small electrical voltage.
The reference electrode provides a constant known voltage as a point of reference. The meter determines the voltage with a formula derived from the Nernst equation and converts it to pH.
The voltage difference created between the electrodes is sent to the electronics of the meter. The meter measures the voltage with a formula from the Nernst equation and changes it into a pH value.
Finally, the level of acidity or alkalinity is measured and displayed on the meter as a pH value. Newer meters may be capable of automatic temperature compensation or calibration.
A pH meter measures the acidity or alkalinity of the solutions accurately in many fields including environmental science, agriculture, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in both experimental and quality control tasks of various laboratories.
A pH meter is used to determine the acidity or basicity of water, soil and wastewater and may provide valuable insight as to the comparative safety of water. It monitors the pollution incidents and provides scientifically sound data on the quality parameters of water, the pollutants and the health of the ecosystem.
Food and beverage industries employ pH meters as instruments that ensure product quality in terms of taste and safety. pH meters are employed during processes such as controlling fermentation, preventing the spoilage of products, and also obtaining products that meet regulatory standards. Precise pH levels ensure consistent textures, flavors, and shelf life in various edible products.
To ensure the stability, efficacy, and safety of medicines, the pharmaceutical industry requires strict pH control. pH meters are employed throughout the process of formulation, testing, and quality assurance. It creates suitable chemical conditions, validates consistency of product attributes, and meets critical regulatory standards.
Laboratory pH meters assist in research, analysis, and various chemical experiments within laboratories. They facilitate studying reactions, making accurate solutions, and testing results for scientists. And it is highly important for acquiring accuracy in the experiment and also to obtain reliable scientific results in different fields.
A pH meter provides a very precise and reliable measurement that is more accurate than the equivalent of a pH strip or pH indicator. In scientific, industrial, and lab biomolecular applications, it’s crucial to have accuracy where variations in pH may influence the quality of your product, the kinetics of a chemical reaction, and, depending on the context, safety. Therefore, this results in a reliable outcome with sensitive applications.
pH meters measure the pH of liquid samples. They can be used in laboratories to monitor and control the quality processes for food or beverage products, cosmetics and chemicals. The stable pH value reduces the possibility of contamination and spoilage inconsistency while working to support regulatory compliance and consumer trust.
To ensure the stability, efficacy, and safety of medicines, the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry requires strict pH control. pH meters are employed throughout the process of formulation, testing, and quality assurance. pH meters help to create suitable chemical conditions, validate consistency of product attributes, and meet critical regulatory determinants related to developing and manufacturing safe medicines.
pH meters are applied in the industrial and environmental agencies to make tests on the drinking water, wastewater, rivers, and soil. Accurate PH values eliminate pollution, imbalance in the ecology, and environmental lawbreaking. The purpose of such analysis is to contribute to public health, aquatic life protection, and the prevention of contamination.
In scientific research and biotechnology, the optimum pH is a critical factor for cell growth, enzymatic activity, and accuracy of experiments. pH meters monitor culture media, chemical reactions, and biological solutions. Their accuracy provides reproducibility of the results, stability of conditions, and success of laboratory outcomes in various disciplines of research.
The pH meter can enhance the workflow for a process because it will give you fast and reliable pH readings with limited human error and variation from your process. This reliability will allow your workflows to run more smoothly, which in turn promotes productivity and reproducibility from batch to batch or experiment to experiment. In the end, this results in reduced guesswork, saving materials that can benefit each process, and improving the management of chemical and biological systems broadly.
To illustrate, we can conceive of pH meters as effective measurements of quality, safety, and consistency, which are regarded as an essential part of a tester in scientific, industrial, agricultural, and environmental contexts. The user’s comprehension of how pH meters function, the state and situation they are functioning in, and what value the pH meter might provide will enable the user to produce informed decisions and correct documentation.
Elevate your quality assurance process to new heights
At Presto, we take pride in being Global manufacturers of Laboratory Testing Instruments for different industries.